
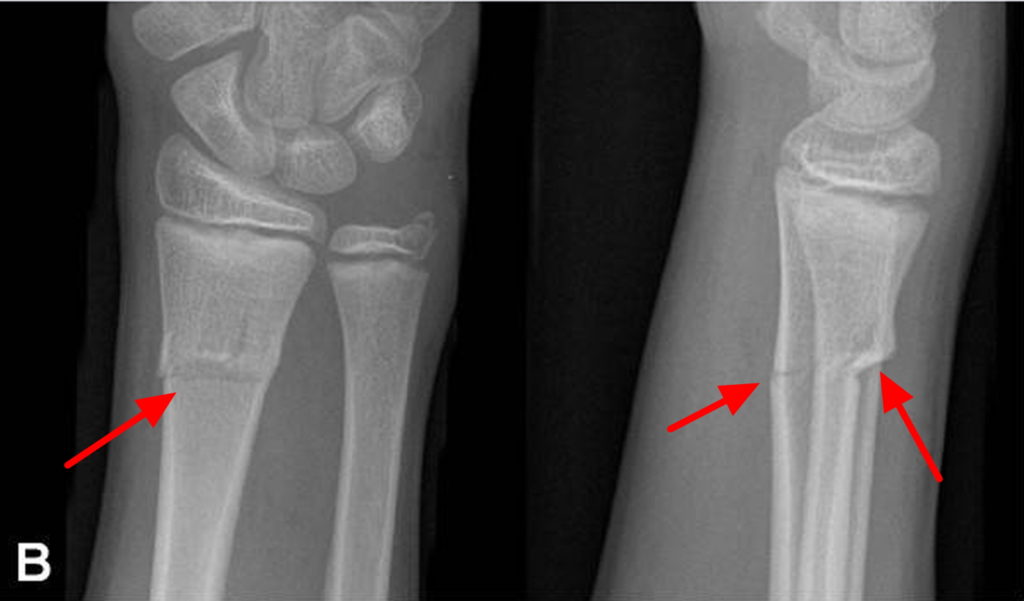
Manage in a wrist splint worn day and night for 3 weeks with no contact sports for a further 3 weeks after splint removal.No greenstick or complete fracture of the ulna (buckle of the ulna is acceptable).Involves the distal third of the radius.Simple dorsal buckle fractures must have ALL of the following features: Simple dorsal buckle fracture of the distal radius and ulna with minimal dorsal angulation X-Ray changes may be subtle with mild cortical bulging on the AP view and angulation on the lateral view may be evident.Buckle (or torus) fractures are most commonly seen in the distal radial metaphysis and are a result of compressive forces from an axial load on softer bones in children.Be aware the scaphoid only starts to ossify at 5 years of age.įor general assessment and management, see Fractures - Overview.
BUCKLE FRACTURE WRIST IN ADULTS SERIES
BUCKLE FRACTURE WRIST IN ADULTS FULL
R ead the full PCH Emergency Department disclaimer. Clinicians should also consider the local skill level available and their local area policies before following any guideline. These clinical guidelines should never be relied on as a substitute for proper assessment with respect to the particular circumstances of each case and the needs of each patient. Clinical common-sense should be applied at all times. They are not strict protocols, and they do not replace the judgement of a senior clinician. These guidelines have been produced to guide clinical decision making for the medical, nursing and allied health staff of Perth Children’s Hospital. Learn more about how doctors diagnose fractures here.Fractures - Distal forearm or wrist Disclaimer It requires urgent specialist care.ĭoctors may use imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, to confirm the diagnosis. Growth plate fracture: This injury, which affects children and teens who are still growing, occurs in the growth plate, usually in the radius near the wrist.Galeazzi fracture: This affects both the radius and the ulna, usually at the wrist, where the two bones meet.This is a more serious fracture that requires emergency care. It can dislocate the top portion of the radius. Monteggia fracture: This affects both the radius and the ulna.Greenstick fracture: This goes through a piece of bone, causing the bone to bend on the other side of the fracture.The broken pieces remain in position and do not separate. Torus or buckle fracture: This causes the top layer of bone to compress, forcing the other side of the bone away from the growth plate.Metaphyseal fracture: This affects either the upper or lower portion of the bone but does not affect the growth plate in children.the treatment plan a doctor might recommendĬommon types of forearm fractures include:.The type of radius or ulna fracture a person sustains will directly affect:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
